



 « Previous | Next » « Previous | Next »
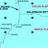
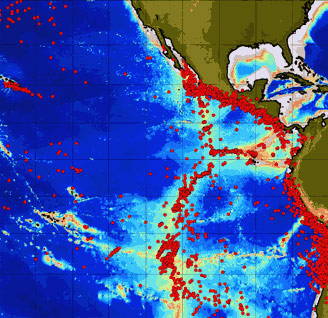
Data collected by the Autonomous Hydrophone
Array in the eastern Pacific Ocean in 1997. Red dots show locations of
earthquakes. Notice how many earthquakes occur along the western coast
of Central and South America. This is due to the plates sliding underneath
the continents and triggering earthquakes and volcanic eruptions on land.
The earthquakes also form a band along the mid-ocean ridge axis. These
are the ones that we will be investigating to find out where and when seafloor
volcanic eruptions have taken place.
Back to AHA »
|