Antarctic: The Frozen Continent
Most people know that Antarctica is the coldest place on Earth, with fewer than 1,000 people living there (none permanently). But did you know it is the world's largest desert? That it hosts huge volcanoes? Has a lake the size of Lake Ontario located entirely beneath the ice? Discover what else you would encounter in Antarctica.
Location/Geography
Imagine flying in a plane over Antarctica, the southernmost continent and the coldest and driest region on earth. From the air, you see that it covers a huge area, about 14 million square kilometers (5.4 million square miles), about half the size of the United States. Antarctica is just slightly larger than another continent in the southern hemisphere, Australia.
You also see that it is quite mountainous. Antarctica has an average elevation of 2,300 meters (6,500 feet) making it the highest continent on Earth.
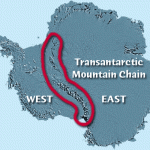
As your plane circles over the landscape, you note that Antarctica is divided into unequal eastern and western portions by the Transantarctic Mountain chain, which is about 100 million years old. East Antarctica is a platform about 1,600 feet (488 meters) above sea level, composed of rocks more than 550 million years old, with younger rocks on top.
West Antarctica lies south of South America. The land in West Antarctica is lower than in the east, and in some places is even well below sea level. The continent’s highest peak, Vinson Massif, is found in West Antarctica. It is located on the coast and is 4,876 meters (16,000 feet) tall.
Under the surface of Antarctica, all is not cold and quiet. In fact, there is an active volcano in Antarctica: Mount Erebus, which is 3,794 meters (12,447 feet) in height, is located in East Antarctica, on the edge of the Ross Ice Shelf—a place where ice extends far out over the ocean.
Antarctica is also home to Lake Vostok, one of the world's largest lakes. Lake Vostok is roughly the size of North America's Lake Ontario, but it is not a lake for sailing boats. It lies 2 miles (4 kilometers) below the continental ice sheet. Its waters have been sealed from air and light under the tremendous pressure of the continental ice sheet for perhaps as long as 35 million years.
Exploration Timeline
not sure what we are doing here.
Ocean Circulation
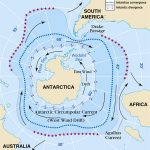
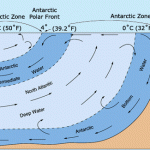
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is the largest wind-driven current on Earth. It is the only current that goes all the way around our planet and connects the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
It is driven by strong westerly winds and creates some of the roughest seas in the world that are notorious to sailors. It was discovered by Edmund Halley, the British astronomer, during the expedition of the HMS Paramore in 1699-1700. Later, James Cook in 1772-1775, and James Clark Ross in 1839-1843 both described the ACC in their journals.
The ACC is a massive flow of water that acts as a barrier separating the Southern Ocean from more northern oceans. The current extends from the sea surface to depths of 4000 m (more than 2.5 miles) and can be more than 120 miles wide. It is a very cold current with temperatures ranging from –1 to 5°C depending on the time of the year, and with speeds up to 2 knots (3.7 km per hour).
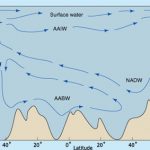
Antarctica is also the place where waters form that flow through the deep ocean as part of the global Ocean Conveyor (World Circulation). Water that flows at the bottom of the ocean is formed on the continental shelf, particularly in the Weddell Sea and the Ross Sea. As ice forms the water becomes saltier (Demonstration). As the ice drifts and gaps open up, the water loses heat and gets colder with temperatures from -0.9°C to +0.4°C (30 to 32°F). Its density increases to become the densest water in the world and it sinks to the bottom of the ocean (below ~4000 m ) to flow throughout the world’s deep ocean.
Different weather conditions a little further north at 45-55°S cause another water mass, called Antarctic Intermediate Water to form. In this area, precipitation is greater than evaporation, so the salinity of the water is low. However, the water gets cooled and sinks to flow through the ocean northward at depths of 600-1000 m.